Enhance Web Browser Security
Steps to enhance the security of your web browser.
This article applies to: Security & Policy
Web browsers are often used for day-to-day work and study. As web browsers have grown increasingly complex, featureful, and essential to many tasks, they have become one of the most common avenues for bad actors to compromise your security.
Follow these guidelines to enhance your web browser security and protect yourself.
Keep Your Browser Updated
Modern web browsers can automatically apply updates or perform them in the background. Make sure you turn on this feature. Restart your browser regularly to apply updates. Major web browsers find and fix new security vulnerabilities about every month. Staying up to date is the only way to stay secure.
- Apple Safari: Update to the latest version of Safari
- Google Chrome: Update Google Chrome
- Microsoft Edge: Update settings
- Mozilla Firefox: Enable background updates
- This Mozilla support article references Windows, but the same setting exists in Firefox for macOS.
Be Mindful of Permissions
Much like modern mobile and desktop operating systems from Apple, Google, and Microsoft, modern web browsers include granular permissions that a website may ask you for, including, but not limited to:
- Displaying pop-ups
- Displaying notifications
- Location access
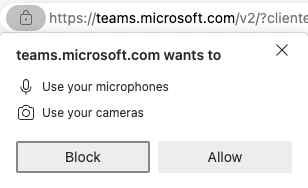
- Camera access
- Microphone access
Malicious websites will often prompt you for these permissions to abuse them. Make sure you block any such prompts unless you are explicitly expecting to use them in a well known application. Examples include granting Microsoft Teams in your browser permission to use your camera and microphone, or granting Google Maps location access.
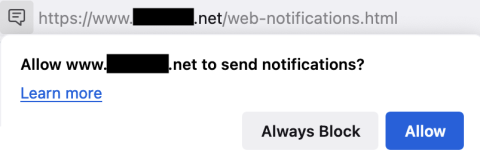
The notifications permission is often abused to send malicious or fraudulent notifications, such as fake browser update notifications or fake virus detection notifications. Block any notification prompts from websites if you do not want their messages.
- Apple Safari: Change Websites settings
- Google Chrome: Change site settings permissions
- Microsoft Edge: Browsing data and privacy
- See the section “How to manage your privacy settings in Microsoft Edge” at the bottom of the page.
- Mozilla Firefox: Site Permissions panel
Be Careful of Browser Extensions
Treat installing a web browser extension as you would any other piece of software or app. Browser extensions can have various permissions, such as reading data from or writing data to webpages, reading cookies stored in your browser, or getting data from your clipboard. These permissions are typically displayed on the extension page before installing and during the installation approval prompt. Verify that an extension is well-known and trustworthy. Check whether the permissions it is asking for make sense for what the extension is doing. Only install browser extensions from your browser’s official extensions store.
Web browser extensions, like other software, can be malicious or may become malicious if sold to a bad actor. Due to their widespread use, web browser extension developers are often contacted by bad actors attempting to purchase rights to their extensions for the purposes of updating them to deliver malware. This was reported by Ars Technica as far back as 2014.
- Apple Safari: Use Safari extensions on your Mac
- Google Chrome: Chrome Web Store
- Microsoft Edge: Edge Add-ons
- Mozilla Firefox: Extensions
Use a Trusted Content-Blocking Browser Extension
One of the most common sources of attempted compromise of a Cornell University device is fraudulent software delivered via malicious advertisements or email links. Consider using a well-known and trusted content-blocking browser extension to protect yourself as advised by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
Some suggestions are available from the resources below.
One particularly well-known and effective option is uBlock Origin.
- Follow the link either at the top of the page or in the “Platforms” section at the bottom to go to uBlock Origin’s page in your browser’s official extension store.
- Users of Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge may instead need to use uBlock Origin Lite due to changes being rolled out over time in the Chromium browser engine project, which these two web browsers are built on.
For Apple Safari there is AdGuard.
Content-blocking extensions may rarely prevent a site from functioning normally. You can typically disable a content-blocking extension for a specific site if you find it is not functioning correctly.
For uBlock Origin
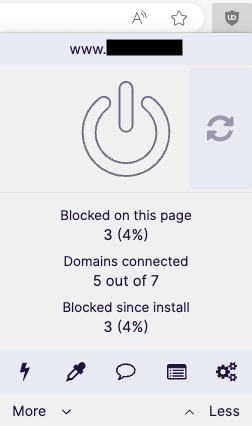
- Click the extension’s red shield icon in your browser.
- Click the large power button to disable the extension for the website you are currently on. The shield icon will turn grey and a "refresh" button will appear beside the power button.
- Click the “refresh” button in uBlock Origin's pop-up window to reload the page or otherwise refresh the page in your browser.
For uBlock Origin Lite
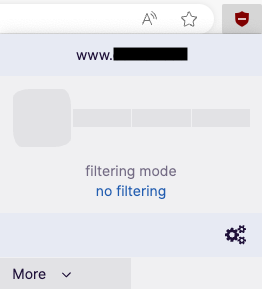
- Click the extension's red shield icon in your browser.
- Click and drag the slider all the way to the left to set the filtering mode to “no filtering”.
- The page will automatically refresh.
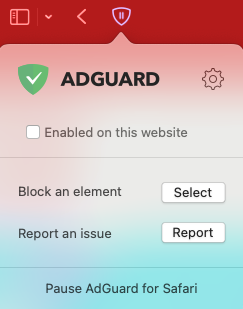
For AdGuard in Apple Safari
- Click the extension’s shield icon in Safari near the URL bar.
- Uncheck “Enabled on this website”
- The page will automatically refresh.
Use Secure Browser Settings
Modern web browser default settings are generally secure. However, your browser may offer additional options for further enhancing your security. Note that these settings, while typically safe to enable, may rarely cause compatibility issues with particular websites. You may need to either exempt these specific websites or change a setting back to its default.
- Apple Safari: Change Security settings in Safari on Mac
- Also see the pages under Table of Contents > Privacy and security
- Google Chrome: Manage Chrome safety and security
- Microsoft Edge: Enhance your security on the web
- Mozilla Firefox: Protect your privacy

Comments?
To share feedback about this page or request support, log in with your NetID